The 2019 Global Internet Phenomena Report, released last month by Sandvine, found that video accounts for over 60% of downstream traffic on the internet. While this percentage is similar to last year's findings, what makes this year's results unique is not necessarily how much more video is being consumed. Instead, as the report lays out, it's about "the shift in where that video is coming from.” Last year's study highlighted the diversity of video streaming worldwide due to the increasing number of providers, and this year's numbers have continued that trend. Sandvine also predicts that these figures will spike again as even more major new services are due to launch soon.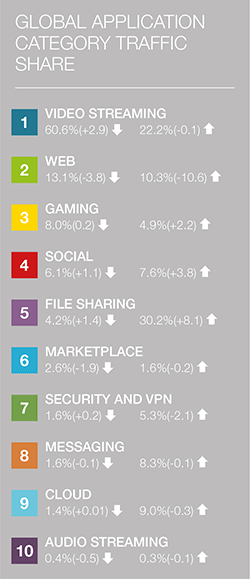 The annual report measures the trends that drive global bandwidth consumption every year, and how consumer behavior changes with market shifts. This year's results account for the first half of 2019. It's also worth noting that high profile events made 2019 a big year for internet traffic, including the final season of HBO's Game of Thrones, the FIFA Women's World Cup, new TV series releases, and new streaming services.
The annual report measures the trends that drive global bandwidth consumption every year, and how consumer behavior changes with market shifts. This year's results account for the first half of 2019. It's also worth noting that high profile events made 2019 a big year for internet traffic, including the final season of HBO's Game of Thrones, the FIFA Women's World Cup, new TV series releases, and new streaming services.
The report found that more consumers worldwide turn to HTTP Media Stream providers—which Sandvine describes as content owners, cable or broadcast channels that stream their content to users—than other streaming services for content: "Some of these services require the user authenticate with a TV provider account to stream traffic (like ESPN does for example), others are simply free to all." HTTP Media Stream accounts for 23.8% of global video streaming traffic, in front of Netflix and YouTube. 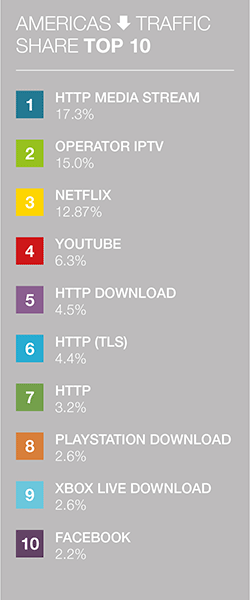 And in the Americas, a similar trend follows with these network services leading the pack. Streaming video and gaming are dominant when it comes to downstream traffic. The findings reveal that as digital gaming's popularity in the region continues to rise, PlayStation and Xbox account for a huge portion of download traffic in the region.
And in the Americas, a similar trend follows with these network services leading the pack. Streaming video and gaming are dominant when it comes to downstream traffic. The findings reveal that as digital gaming's popularity in the region continues to rise, PlayStation and Xbox account for a huge portion of download traffic in the region.
All of these trends indicate that more bandwidth availability in the near future will be of utmost necessity in order to accommodate the content demands that consumers crave, whether that be for the large screen in their homes, long form video, gaming, or new entertainment experiences. 4k and 8K will also require faster speeds as they become more popular with consumers. As the report states, "Even more frightening is that 4K content streams are a drop in the bucket so far, and 8K is not yet a reality—when it is, all bets are off!"
Fortunately, the industry is already hard at work to deliver ultra-fast gigabit internet not too long from now. The 10 gigabit speeds that cable ISPs will provide will continue to revolutionize the marketplace as new innovative products and services promise to entertain and delight viewers every year.
For more information on the cable industry's 10G initiative, visit: https://www.10gplatform.com/
